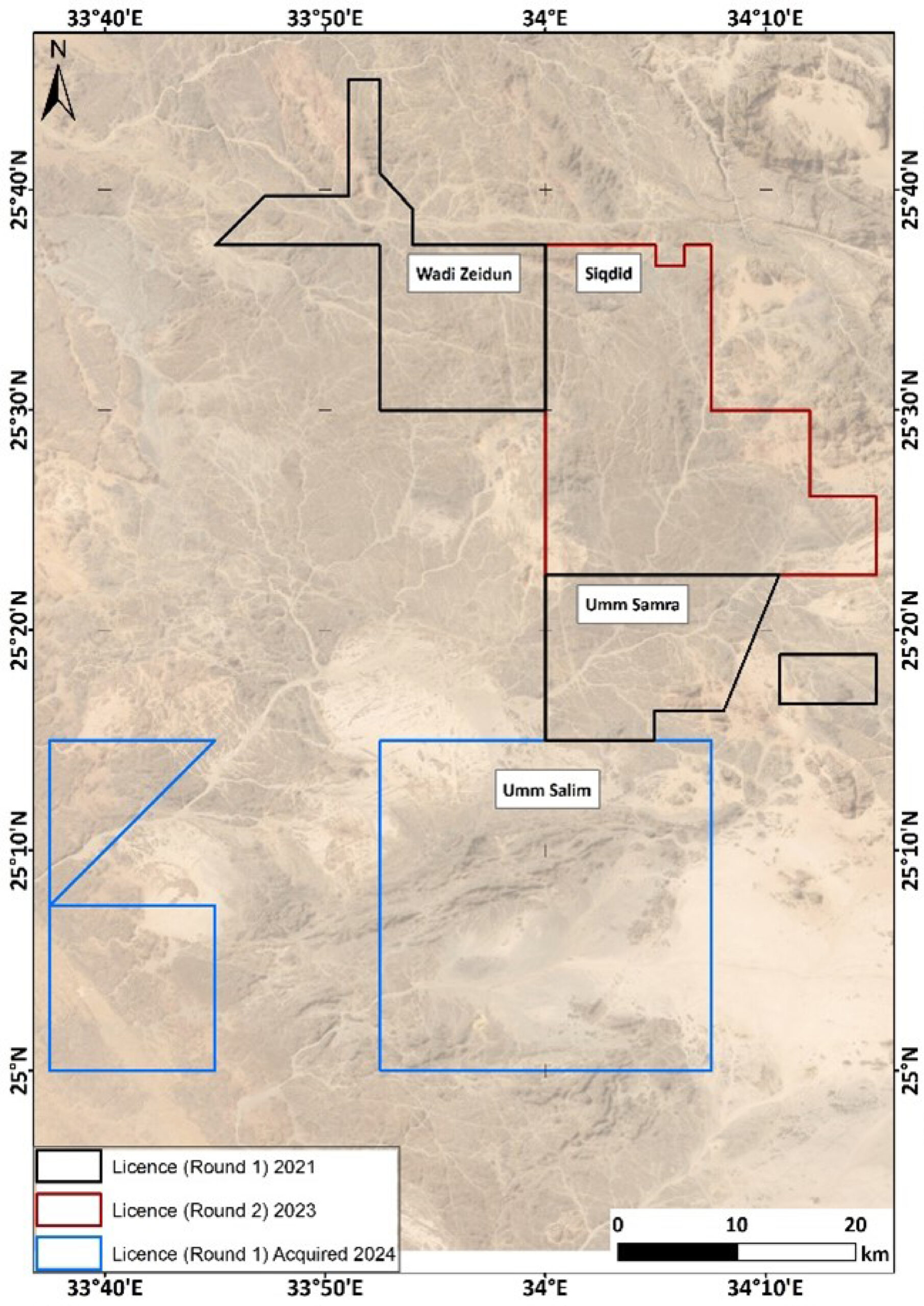
In two competitive international bid rounds, Lotus Gold secured ten exploration sectors (blocks or licenses) across the Egyptian Eastern Desert. Subsequent renewal and relinquishment of blocks, as well as the addition of 5.5 blocks acquired from B2Gold brings the total land position to ±1,930 km2 (roughly the equivalent of 11 blocks), as summarised below:
| Exploration Agreement | Project Area | # of Exploration Sectors | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BR1 – Zeidun | Wadi Zeidun | ±1.4 (after renewal) | 253 |
| BR1- Umm Samra | Umm Samra | ±1.3 (after renewal) | 230 |
| BR2 – Siqdid | Siqdid | 3 | 483 |
| (BR-1) – Umm Salim | Umm Salim | 5.5 | 963 |
| Total | ±11 | ±1,930 |
LOTUS CENTRAL EASTERN DESERT ±1,930 km² CONTIGUOUS LAND HOLDINGS
The geology of Egypt is dominated by Mesozoic and Quaternary sediments which cover most of the center and west of the country. The exception is the Eastern Desert, located between the River Nile and the Red Sea, and Southern Sinai, where Precambrian rocks of the Arabian-Nubian Shield (ANS) are seen in outcrop. The ANS is a geological terrane which extends across Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Eritrea, Ethiopia and Yemen. These Precambrian units represent a Neoproterozoic orogenic cycle, dated between 870 Ma – 540 Ma. The area hosts Egypt’s only significant operating gold mine, Centamin’s Sukari mine (producing +400K ounces gold per annum, with +5M ounces produced to date) and situated 60km west of the Lotus projects.
The ANS stratigraphy can be divided into distinct geological phases:
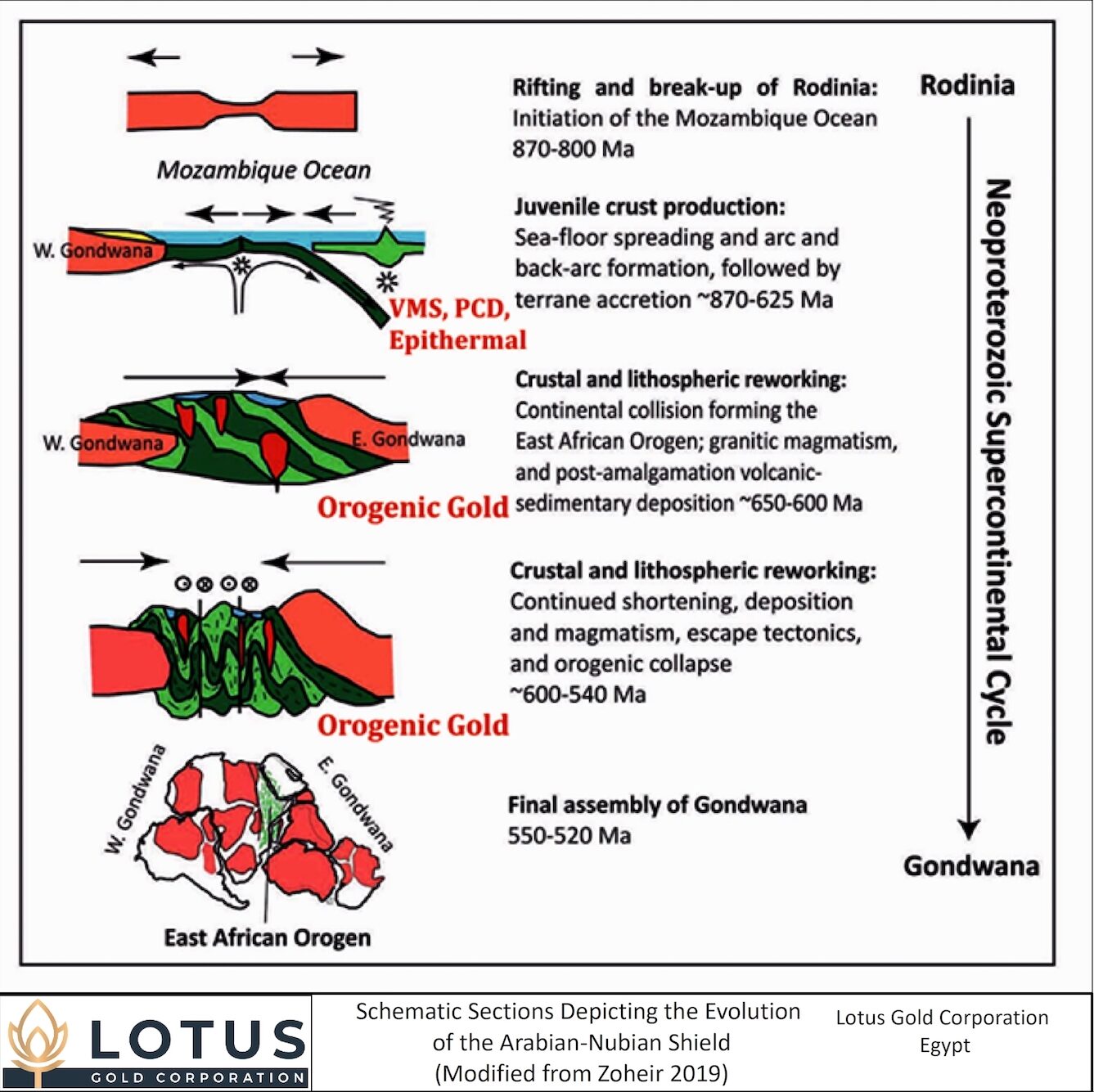
The mineral endowment of the ANS includes Porphyry/Epithermal systems and VMS deposits, formed during earlier oceanic and Island Arc phases, and later Orogenic Gold associated with the collisional and post collisional phases. The ANS as a region has attracted significant interest from industry players including Centamin, Barrick, B2Gold, Aton Resources, Perseus Mining (Orca Gold), Managem, Pan African Resources, Zijin Mining, Ivanhoe Electric, Vedanta.
Significant mining projects within the ANS include:
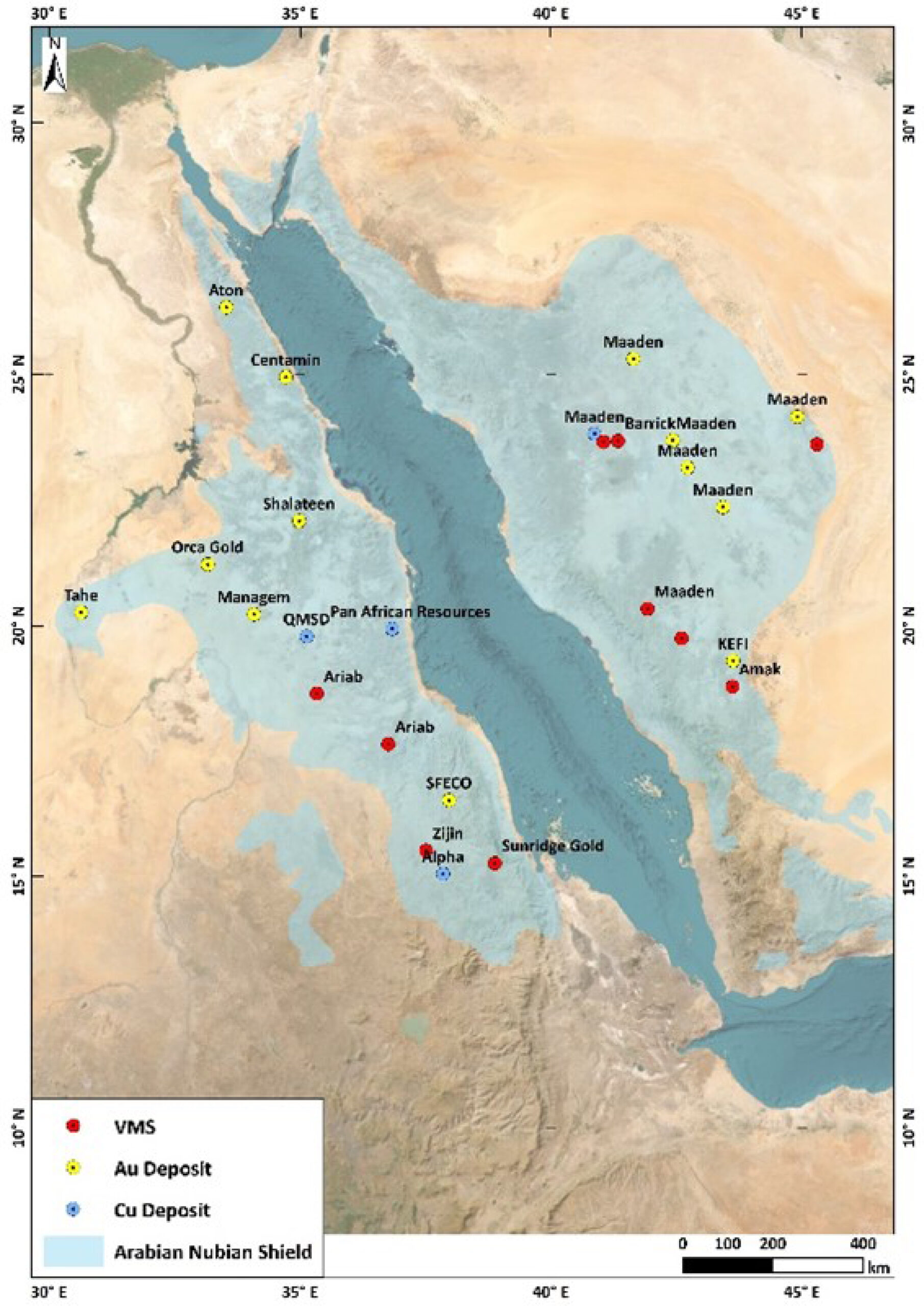
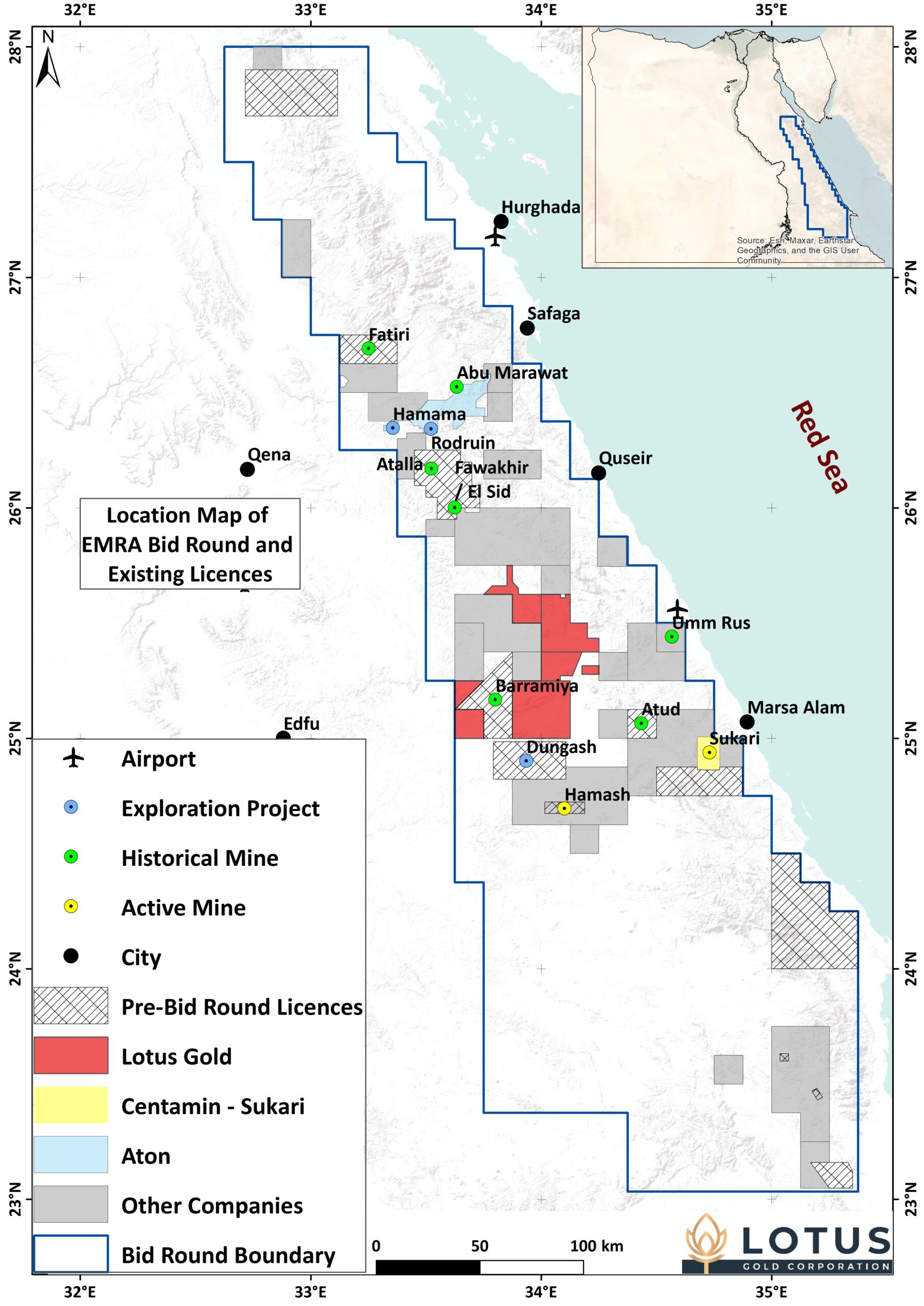
Within Egypt, the Eastern desert is subdivided into three geological terranes known as the Central Eastern Desert (CED), Northern Eastern Desert (NED) and Southern Eastern Desert (SED). The CED and to a lesser extent the NED are the main focus of current exploration and mining activity in Egypt. The location of Lotus’ license areas within the Eastern Desert are shown in the figure below.
The NED is dominated by granitoids and is regarded as having potential for porphyry-epithermal systems and to a lesser extent orogenic gold. The CED is dominated by major structural events, in particular WNW to NW trending Najd and E to ENE trending Mubarak-Barramiya structures. Both structural orientations are associated with orogenic gold mineralization. The SED is separated from the CED by a major Najd fault structure (the Nugrus Fault) and shows similar geology to that seen to the south in Sudan. The Allaqi-Heiani and Onib-Sol Hamed suture zones (plate boundaries) lie close to the Sudanese border and are associated with orogenic gold mineralization.